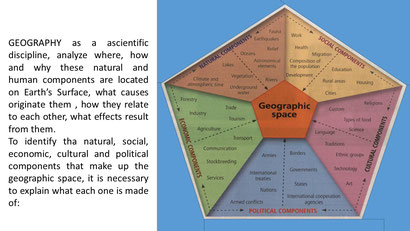
GEOGRAPHICAL SPACE:
IT DEFINES SPACE ORGANIZED BY SOCIETY-HUMAN GROUPS IN THEIR INTERRELATION WITH THE ENVIRONMENT.
Geographic space is composed of natural elements such as vegetation, soil, mountains and bodies of water, as well as social or cultural elements, that is, the economic and social organization of people and their values and customs.
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GEOGRAPHIC SPACE
C - A - R - D - D
CHANGING: This means the geographic space is transformed because it is part of physical or human processes of short, medium and long duration that modify it incessantly. For example, the actions of the rain, wind or waves, or due to the construction of bridges, highways, cities, ports, agricultural fields, etc.
ACCESSIBLE: Any geographic space in the world has a location, be it absolute (that is defined by its geographic coordinates: latitude, longitude and altitude) or relative (that is determined by its situation regarding other spaces abd taking as a reference the cardinal points: North, South, East and West)
RELATIONSHIP: It is the degree of connection between the natural and human components of the geographic space, which implies that the components are not isolated: if one of them is altered, one way or another, it will have effects on the other, be it in the short, medium or long run. For example, excessive logging, air, water and soil pollution, or the loss of biodiversity.
DISTRIBUTION: It's the way that natural and human components are distributed in the geographic space. It is classified by density, which describes the number of times a component appears on a specific surface (for example, people per square kilometer, people/km2); by concentration or dispersion, which indicates how close or how separated the components are, or by patterns, meaning, if there is an element that influences the location of the components, such as rivers or cities.
DIVERSE: It refers to the variety and differences regarding quantity, characteristics and organization of natural, social, economic, political and cultural components that distinguish a geographic space from another. A representative example is the contrast between the countryside (rural areas) and the city (urban areas)
 GEOGRAPHY
GEOGRAPHY